

Beginning with Windows 7, Microsoft limited AutoRun to CD and DVD drives, updating previous Windows versions. The AutoRun feature of Windows worked on all removable media, allowing USB storage devices to become a portal for computer viruses. Only memory cards (not internal-storage memory) can generally be exported, due to file-systems issues see device access, below.
However, third-party applications add MSC emulation to most WM devices (commercial Softick CardExport and free WM5torage). A Windows Mobile device cannot display its file system as a mass-storage device unless the device implementer adds that functionality. However, portable devices typically cannot provide enough power for hard-drive disk enclosures (a 2.5-inch (64 mm) hard drive typically requires the maximum 2.5 W in the USB specification) without a self-powered USB hub. Windows Mobile supports accessing most USB mass-storage devices formatted with FAT on devices with USB Host. Windows 2000 has support (via a generic driver) for standard USB mass-storage devices Windows Me and all later Windows versions also include support.
USB MASS STORAGE DEVICE DRIVER FREE DRIVERS
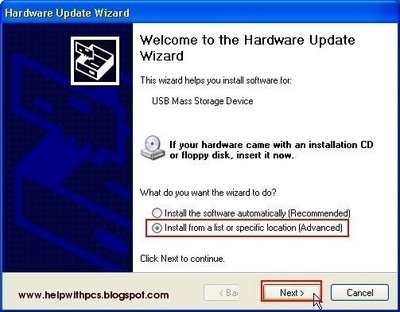
Third-party, freeware drivers became available for Windows 98 and Windows 98SE, and third-party drivers are also available for Windows NT 4.0. During that time no generic USB mass-storage driver was produced by Microsoft (including for Windows 98), and a device-specific driver was needed for each type of USB storage device.
USB MASS STORAGE DEVICE DRIVER FREE UPDATE
Windows 95 OSR2.1, an update to the operating system, featured limited support for USB. There is no support for USB supplied by Microsoft in Windows before Windows 95 and Windows NT 4.0. Microsoft Windows has supported MSC since Windows 2000. Most mainstream operating systems include support for USB mass storage devices support on older systems is usually available through patches. While MSC is the original abbreviation, UMS (Universal Mass Storage) has also come into common use.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
